Eye health is often taken for granted, yet our eyes play a vital role in almost everything we do—from reading and driving to working and enjoying time with family. Despite their importance, many people don’t think about caring for their vision until problems begin to appear. Two of the most common eye conditions worldwide are glaucoma and cataracts, both of which can quietly develop over time and lead to significant vision loss if left untreated. Because these conditions often progress slowly and without obvious symptoms in the early stages, regular awareness and checkups are crucial.
In this blog post, we’ll explore how to recognize the early warning signs of glaucoma and cataracts, understand why early detection can make a life-changing difference, and learn practical steps you can take to protect and preserve your vision for years to come.
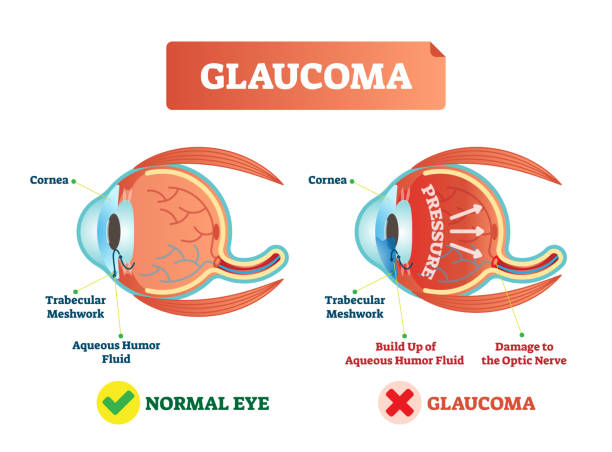
What Is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is not just a single disease, but a group of eye conditions that gradually damage the optic nerve—the vital structure responsible for transmitting visual signals from the eye to the brain. In many cases, this damage is linked to increased pressure inside the eye, known as intraocular pressure. When this pressure becomes too high, it can slowly harm the delicate nerve fibers of the optic nerve.
Because the optic nerve plays such a crucial role in vision, any damage to it can lead to irreversible vision loss. What makes glaucoma especially concerning is that it often develops without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. Many people may not realize there is a problem until significant vision has already been lost. This is why understanding glaucoma and detecting it early are essential steps in protecting long-term eye health.
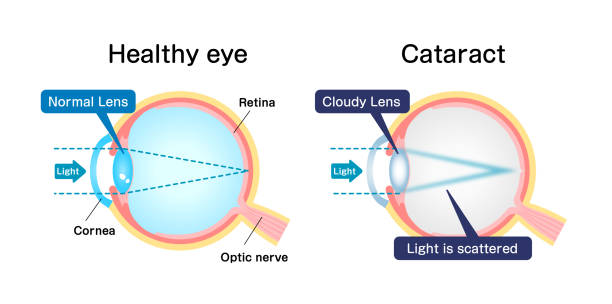
What Are Cataracts?
Cataracts occur when the natural lens of the eye gradually becomes cloudy or opaque. The lens is normally clear and flexible, allowing light to pass through and focus properly on the retina so you can see sharp, detailed images. When a cataract forms, this clarity is reduced, making vision appear blurry, hazy, or dim—almost like looking through a foggy window.
Cataracts typically develop slowly over time, which means changes in vision may be subtle at first. Colors may seem faded, lights may appear too bright or create glare, and night vision can become more difficult. While cataracts can develop for various reasons, including injury or certain medical conditions, they are most commonly associated with aging and are especially prevalent among older adults. With proper monitoring and treatment, cataracts can be effectively managed to restore clear vision.
Early Signs of Glaucoma
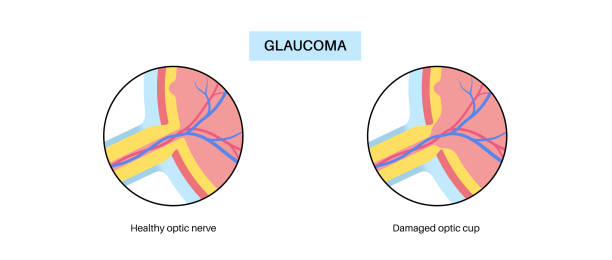
Glaucoma can be tricky because it doesn’t always show obvious symptoms at first. It is often referred to as the “silent thief of sight” because it can cause gradual vision loss without pain. That’s why it’s important to keep an eye on any changes in your vision. Here are some early signs of glaucoma:
- Gradual Loss of Peripheral Vision
The first signs of glaucoma usually affect your peripheral (side) vision. You might notice that your vision feels narrower or that you have trouble seeing things off to the side, especially in low-light situations. - Blurry Vision
If you experience blurry or hazy vision, especially when looking at things in the distance or when reading, this could be an early sign of glaucoma. It’s important to note that blurry vision might also be caused by other eye issues, so seeing an eye doctor is crucial for a correct diagnosis. - Haloes Around Lights
People with glaucoma may notice haloes or rainbow-colored circles around lights, especially at night. This happens because of pressure on the optic nerve, which distorts how light enters the eye. - Eye Pain or Redness
Although not all people with glaucoma experience pain, some may notice pain in or around the eyes. Redness, especially when accompanied by pain or nausea, can be a sign of acute glaucoma, which requires immediate medical attention. - Sudden Vision Loss
In some cases, glaucoma can cause sudden vision loss, often in one eye. If this happens, it’s important to seek medical help right away to prevent permanent damage.
Early Signs of Cataracts
Cataracts tend to develop slowly, and it may take years before they significantly affect your vision. The good news is that cataracts can be treated with surgery if caught early. Here are some signs that you may have cataracts:
- Blurry or Hazy Vision
One of the first signs of cataracts is blurry vision. If objects appear cloudy or you notice halos around lights, especially at night, it could be a sign of cataracts. This happens because the lens of your eye becomes cloudy and scatters light entering the eye. - Difficulty Seeing at Night
As cataracts develop, they can make it harder to see in low-light situations. This is especially noticeable when driving at night, as headlights and streetlights can appear blurry or overly bright. - Frequent Changes in Prescription Glasses
If you find yourself needing new prescription glasses or contacts more often, it could be a sign of cataracts. The lens of your eye changes shape and becomes cloudier as the cataract develops, affecting your vision. - Fading or Yellowing of Colors
Another common symptom of cataracts is a change in how colors look. You may notice that things appear more yellow or that colors seem duller than they used to. This happens because the lens of the eye loses its ability to filter light properly. - Double Vision in One Eye
Double vision in one eye, or diplopia, is another early sign of cataracts. This can make it difficult to focus clearly on objects and may worsen as the cataract progresses.
Why Early Detection Is Important
Both glaucoma and cataracts have the potential to cause serious vision problems—and in severe cases, even permanent blindness—if they are not properly diagnosed and treated. Because these conditions often develop gradually, many people may not notice the warning signs right away. Unfortunately, waiting until vision becomes noticeably impaired can limit treatment options and outcomes. That’s why early detection plays such a critical role in protecting long-term eye health.
In the case of glaucoma, damage to the optic nerve cannot be reversed, but early diagnosis and treatment—such as medicated eye drops, laser therapy, or other procedures—can significantly slow or even prevent further nerve damage. Acting early helps preserve remaining vision and reduces the risk of progression.
For cataracts, treatment is highly effective. When vision becomes significantly affected, a relatively quick and common surgical procedure can remove the cloudy natural lens and replace it with a clear artificial lens. Cataract surgery has a high success rate and can dramatically restore clarity, brightness, and overall quality of vision. With regular eye exams and timely care, the impact of both conditions can be greatly minimized.
How to Protect Your Eyesight

While you can’t always prevent glaucoma or cataracts, there are steps you can take to protect your eye health:
- Get Regular Eye Exams
The best way to catch glaucoma and cataracts early is by scheduling regular eye exams with an eye care professional. A comprehensive eye exam can help detect these conditions even before symptoms appear. If you’re over 40 or have a family history of eye disease, it’s especially important to have eye exams every two years. - Wear Sunglasses
Protect your eyes from harmful UV rays by wearing sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays. Prolonged sun exposure can increase the risk of cataracts, so it’s essential to shield your eyes when outside, even on cloudy days. - Maintain a Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can help keep your eyes healthy. Foods like leafy greens, fish high in omega-3 fatty acids, and fruits rich in vitamins C and E are great for eye health. - Stay Active and Manage Health Conditions
Exercise is beneficial for overall health, including eye health. Regular physical activity can help control blood pressure and reduce the risk of developing glaucoma. If you have health conditions like diabetes, keeping them under control can also reduce your risk of cataracts and glaucoma. - Quit Smoking
Smoking is linked to an increased risk of cataracts and other eye problems. If you smoke, quitting can help reduce your risk of developing these conditions.
Conclusion
Being aware of the early warning signs of glaucoma and cataracts is one of the most important steps you can take to protect your eyesight. Subtle changes—such as blurred vision, increased sensitivity to light, difficulty seeing at night, or gradual loss of peripheral vision—should never be ignored. Even if the changes seem minor, they may signal the beginning of a more serious condition. Seeking professional care at the first sign of vision problems can make a significant difference in preventing long-term damage.
Scheduling regular comprehensive eye exams is equally important, even if you feel your vision is fine. Many eye conditions, especially glaucoma, can develop silently without noticeable symptoms in the early stages. An eye doctor can detect problems early through specialized tests and recommend appropriate treatment before significant vision loss occurs.
In addition to routine checkups, maintaining healthy lifestyle habits—such as eating a nutrient-rich diet, protecting your eyes from UV exposure, managing chronic conditions like diabetes, and avoiding smoking—can further reduce your risk. By staying proactive and informed, you can greatly lower the chances of vision loss from these common eye conditions and continue to enjoy clear, healthy eyesight for many years to come.