What diabetes is and how does it affect the body?
Diabetes is a disease that affects how the body uses glucose (a type of sugar). Glucose levels in the blood need to be controlled for a person to stay healthy. Blood glucose levels are regulated by insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas.
In diabetes, either not enough insulin is produced or the body cannot use insulin properly. This causes high blood sugar which can lead to damage to the heart, blood vessels, and kidneys if not treated properly.
In most cases, there is no known cause for Type I Diabetes although it tends to run in families without being directly inherited from them. In Type II Diabetes, the most common form, people with obesity and those over 60 years old have a greater risk of developing it as they are less likely to be physically active and tend to make poor dietary choices.
Type II diabetes usually starts as insulin resistance, a condition where muscle, liver, and fat cells do not use insulin properly leading to high levels of blood glucose. Although there is no cure for Type I or Type II Diabetes, it can be controlled with proper diet and exercise.
What are the different types of diabetes treatments available?
• Injections
• Oral Medications
• Insulin Pumps
Injections: There are two types of injections used to manage Type I and Type II Diabetes. The first type is long-acting insulin which controls high blood sugar throughout the day and night, usually given once a day. The other type is rapid-acting insulin which helps control high blood sugar levels after eating, usually given right before or with meals. This may be combined with long-acting insulin to keep the level of glucose in the blood as close to normal as safely possible throughout the whole day and night.
Oral medications: Sulfonylureas lower blood glucose by causing the pancreas to release more insulin into the body so this type of medication is only used if synthetic insulin does not work for a person or if they are unable to inject themselves. This type of medication has many side effects which makes it less popular than other medications. Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) receptor agonists lower blood glucose levels by causing the pancreas to slow down the amount of insulin released into the body and also slowing down how quickly food moves from the stomach to the intestines.
Insulin pumps: Insulin pumps are small devices that give insulin at steady rates throughout the day and night (similarly like someone with Type I Diabetes would do on their own). The pump can be attached to the hip, stomach, arm, back of the waist, or buttocks with a small flexible tube that is inserted into the skin. A small plastic piece with a needle is attached to the tubing and covered by a standard bandage.
How to choose the best treatment for you?
When choosing a treatment plan, you should discuss all your options with a physician to decide what will work best for you.
If someone has Type I diabetes and is having trouble controlling their blood sugar, an insulin pump can be used in addition to injections of either long-acting or rapid-acting insulin depending on the person’s needs. It may also be used by people who have Type II diabetes that is not well controlled when taking oral medications alone.
In patients with high cholesterol, Metformin (a medication commonly prescribed in Type II Diabetes) may decrease the chances of heart attacks in both men and women without increasing weight gain. The drug does not have any effect on obesity itself but it does improve blood pressure and body mass index making weight gain less of an issue.
For people with severe insulin resistance, Metformin may decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease by about 15% for every 23 mg/dl (1 mmol/L) reduction in fasting plasma glucose levels within 3 months. It is not effective for lowering blood pressure or cholesterol levels however it may reduce the risk of developing diabetes by 25%.
How to manage your diabetes treatment plan?
The best way to manage diabetes treatment is by having a healthy lifestyle including a healthy diet and regular exercise.
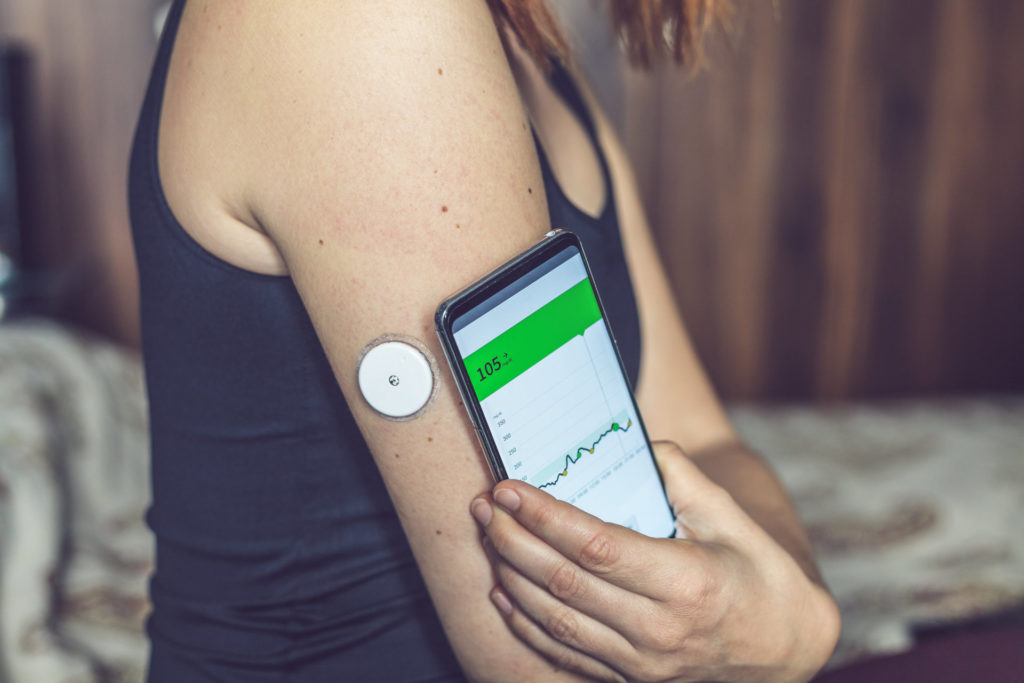
In addition, you should monitor your blood sugar levels carefully because the combination of medications used can affect how often you need to check your blood sugar levels and adjust insulin dosages appropriately. If needed, making changes in insulin dosages should be done gradually. A doctor may also want you to check more frequently if your blood glucose level is outside of the target range or if there are sudden increases or decreases in your level.
What are some common side effects?
The most common side effects include:
- Digestive problems such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation
- Bloating
- Fatigue
- Frequent and/or watery bowel movements
- Dizziness and loss of consciousness (especially if combined with other Type II Diabetes medications)
In addition to this, Metformin can cause vitamin B12 deficiency so those on this medication should have their levels checked every one to three years. In rare cases, Metformin may cause a life-threatening condition called lactic acidosis or liver problems. If you experience any of these side effects, talk to your doctor about changing the way you take your diabetes treatment.
Tips for living well with diabetes.
- Monitor your blood glucose levels regularly
- Eat healthily and exercise regularly
- Talk to your doctor about any concerns or questions you have so you can live well with diabetes.
What is the best way to live a healthy life?
To live a healthy life, one should eat a balanced diet and exercise regularly. Keeping track of what you put into your body helps maintain or lose weight if needed, which can greatly reduce someone’s risk for developing Type II Diabetes. People who have been diagnosed with diabetes need to pay extra attention to their health as some medications used to treat it such as Metformin may cause side effects such as nausea and loss of energy (fatigue). If this occurs, tell your physician immediately as they may be able to prescribe you another medicine.
If your blood sugar levels are too high, exercising can help lower them by increasing the amount of glucose being taken up by the muscle cells. However, it’s important to talk to a doctor before starting an exercise plan if you have diabetes because some exercises may have dangerous effects on your body when combined with medications.
What is a healthy diet?
A healthy diet includes a balance of lean protein, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables while avoiding foods that are high in saturated fat and sugar such as soda and candy. Eating on a schedule helps maintain balanced blood sugar levels throughout the day while eating small portions more often will help avoid becoming overly hungry which could lead to unhealthy snacking. A doctor or nutritionist may be willing to help you develop a diet plan that fits your specific needs.
People with diabetes should avoid eating sugary foods as they can contribute to causing elevated blood sugar levels, especially if coupled with a sedentary lifestyle. Saturated fats and trans-fats also affect the cardiovascular system so it’s important to maintain a healthy balance of fat in one’s diet. Excessive intake of saturated fats makes cells less sensitive to insulin which over time may contribute to the development of Diabetes Type II.
Diabetes is a serious disease that can lead to health complications if left untreated. When choosing a treatment plan, it’s important to discuss all your options with your physician so you can find the best way to manage diabetes for you. A healthy lifestyle is key in managing diabetes – this includes eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise. People with diabetes should avoid eating sugary foods as they can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels. If you have diabetes, making simple changes like these to your lifestyle can make a big difference in keeping your blood sugar levels under control.



